Fe-based high-temperature superconductivity: Impact of atomic defects in the electronic states
REVIEW
Abstract
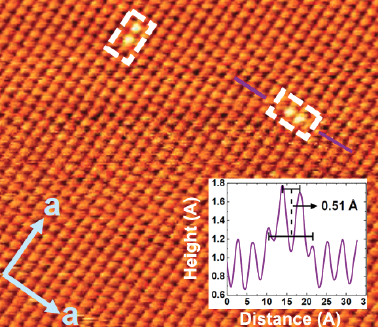
A brief review on the impact of atomic defects in the electronic properties of Fe-based super conductors is hereby presented, focusing in particular on the FeSe family of superconductors. This family of compounds captured the attention of the scientific community during the last decade since its simple crystal structure seemed to be an advantage in understanding the microscopic mechanisms mediating high-temperature superconductivity in Fe-based superconductors. Now, more than 14 years of intense research around the world have elapsed since the discovery of the so-called iron age of superconductivity, and nevertheless it is still debated which is the origin of superconductivity in these compounds. One thing stands for certain in all the enquiries: There is a subtle interplay between defects or local variations in the crystal structure and the electronic states in Fe-based superconductors. This review presents an overview on the main contributions of the community in this interplay in the particular case of the FeSe family and provides a critical discussion on some of the points that still need to be studied in order to provide a thorough quantitative understanding of this issue.